- PDF
2. Adjust Feedback Threshold
- PDF
In the following you will learn:
What a feedback similarity threshold is.
Why feedback has less effect after a while.
Which is why you have to increase the threshold to ensure the quality of the response.
💡The closer the value is to 1, the more likely the feedback given will be taken into account in a similar search query. Recommendation: 0.85 - 0.95.
To adjust the feedback threshold, navigate to Algorithm — > AI Settings
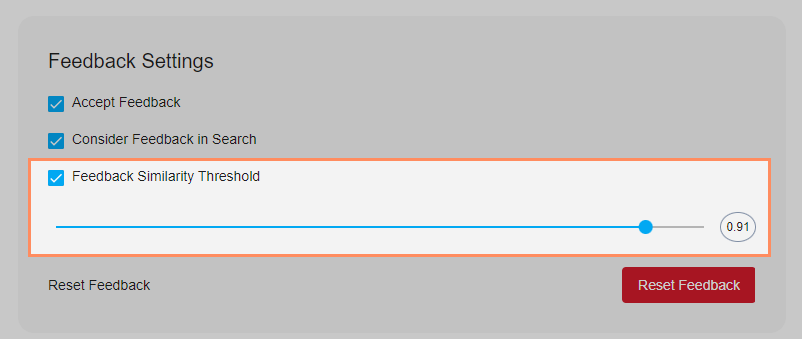
1) How does the Feedback Similarity Threshold work?
When the AI's response is evaluated or corrected, the correct feedback is stored.
In the future, the AI will check: "Is the new user question semantically similar enough to the feedback?"
This similarity is controlled by a threshold :
Low threshold → Even rough similarities are enough, feedback is often applied.
High threshold → Only very close (semantically "dense") hits are used.
2. Why does feedback no longer work after some time?
In the beginning:
Users give a lot of new feedback → even with a low threshold there is a clear learning effect.
Every correction noticeably improves the answers.
After some time:
The system has already learned many similar cases.
With a low threshold, it matches feedback even to vaguely similar questions.
The result: The feedback is applied too broadly → it is watered down, it does not appear precise, and the quality stagnates.
3. Why does the threshold need to be increased?
As the amount of feedback increases, the "density" in the embedding memory grows.
In order to use relevant and really appropriate feedback, you have to tighten the threshold.
As a result, the AI ignores inaccurate feedback that does not fit 1:1.
This prevents quality from stagnating or even deteriorating due to incorrect overuse of feedback.
4. Analogy to the explanation
Imagine sorting screws into boxes by size:
Initially, large categories (small, medium, large) are sufficient. → It helps immediately.
Later, when you have many different screws, this rough division is no longer enough.
You need finer categories (10 mm, 12 mm, 14 mm ...).
This is exactly what the higher similarity threshold does: it ensures more precise fits so that the feedback is effective.
5. Conclusion
In the beginning: low threshold → feedback seems broad, fast learning curve.
Over time: more feedback data → low threshold dilutes → quality stagnates.
Solution: Increase the threshold so that only really suitable feedback takes effect → the answers become more precise again.

